
Research objective: To evaluate whether existing Facility-Based Community Health Workers (FB-CHWs) and Female Community Health Volunteers (FCHVs) of Ministry of Health can collaboratively diagnose hypertension and initiate/maintain protocol-based hypertension treatment with amlodipine and contribute to a reduction of blood pressure among untreated hypertensive patients at baseline.
Research method: Quantitative
Study design: It is a quasi-experimental pre-post study design.
The research method is quantitative with the primary outcome is the net change in systolic blood pressure. The secondary outcome is a change in diastolic blood pressure, the proportion of hypertension control (systolic <140 and diastolic <90 mmHg).
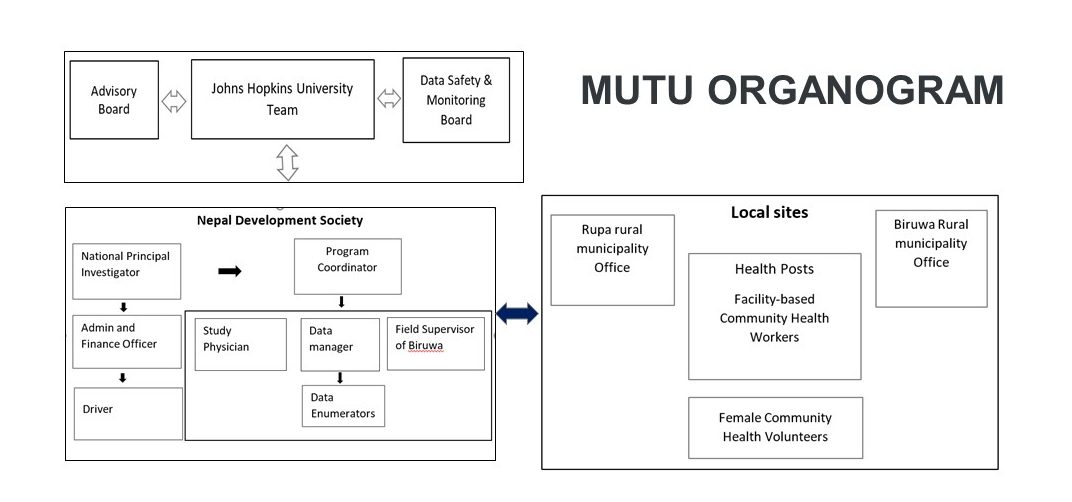
Study site: Rupa Rural Municipality of Kaski District, located in the Gandaki Province of Nepal and Biruwa Rural Municipality of Syangja District in the Gandaki Province.
Study Population: All the adults aged 25-70 years of age and who are permanent residents of the Rupa and Biruwa municipalities.
Procedures: Facility based-community health workers (Fb-CHWs) and Female community health volunteers (FCHVs) both go through extensive training regarding the burden of hypertension; risk factors of hypertension; blood pressure measurement by a digital BP device, referral procedures; personalized health promotion counselling on lifestyle changes; and recording, reporting, and follow-up procedures. FB-CHWs receive training on initiating the treatment of hypertension using amlodipine based on the study protocol.
Ethical consideration: Ethical approval is obtained from Nepal Health Research Council. Written consent will be received from the participants prior to data collection.
Data safety and monitoring board: Is formed and regularly updated.


Validity and Reliability of the Study Tools: The WHO STEP Survey tool is taken as a reference material for baseline and follow-up survey which was validated and previously used by Nepal Health Research Council.
Expected outcome: This study is the first of its kind to evaluate the possibility of utilizing the trained community health workers to reduce the burden of hypertension in LMIC. If our study shows that the intervention is effective, a scaled-up approach could produce an important reduction in cardiovascular disease burden due to hypertension in Nepal.